Problem Statement


🧬 Problem Statement – Fun & Educational Summary
This project explores a fascinating biological mystery: how brown bears survive months of inactivity during hibernation with almost no muscle loss, while humans and other non-hibernating animals rapidly lose muscle under similar conditions. The core idea is that circulating factors in bear blood (serum) may actively protect muscle and metabolism during hibernation.
To test this, the study establishes C. elegans as a model organism and examines how bear serum affects worm physiology and behavior, with a special focus on seasonal differences between summer and winter serum. Below is a complete breakdown of all topics addressed in the problem statement .
🐻 Biological Background: Why Bears?
- Brown bears remain inactive for months during hibernation.
- Despite prolonged immobility, they:
- Show minimal muscle atrophy
- Wake up metabolically healthy
- This is dramatically different from humans, where inactivity leads to muscle wasting, mitochondrial dysfunction, and metabolic decline.
- Hypothesis: hibernation-specific factors in bear serum actively maintain muscle and cellular health.
🧪 Central Research Hypothesis
The project tests whether serum-borne factors in brown bear blood:
- Have detectable biological effects when fed to C. elegans
- Differ between summer and winter, reflecting the bear’s physiological state
In short: 👉 Can bear serum “transfer” aspects of hibernation biology to worms?
🧫 Why C. elegans?
C. elegans is chosen because it:
- Is genetically tractable 🧬
- Has well-characterized muscle, mitochondria, and behavior
- Responds robustly to dietary and environmental cues
- Can enter dauer, a stress-resistant, low-metabolism state (conceptually similar to hibernation)
This makes it a powerful system to probe systemic, serum-driven effects.
🧠 Key Experimental Questions
1️⃣ Does brown bear serum affect C. elegans at all?
- Worms are fed brown bear serum
- Researchers look for any measurable phenotypic changes
- This establishes whether serum components remain biologically active across species
2️⃣ Are winter and summer bear serum effects different?
- Serum is collected from:
- 🟢 Summer bears (active, feeding)
- 🔵 Winter bears (hibernating)
- The study tests whether:
- Seasonal physiological states of bears are reflected in serum composition
- These differences cause distinct outcomes in worms
This directly links seasonal biology → blood composition → organismal phenotype.
🔬 Phenotypes Investigated in C. elegans
💪 Muscle Fiber Structure
- Examines whether serum:
- Preserves muscle organization
- Alters muscle integrity or size
- Directly parallels muscle atrophy resistance in hibernating bears
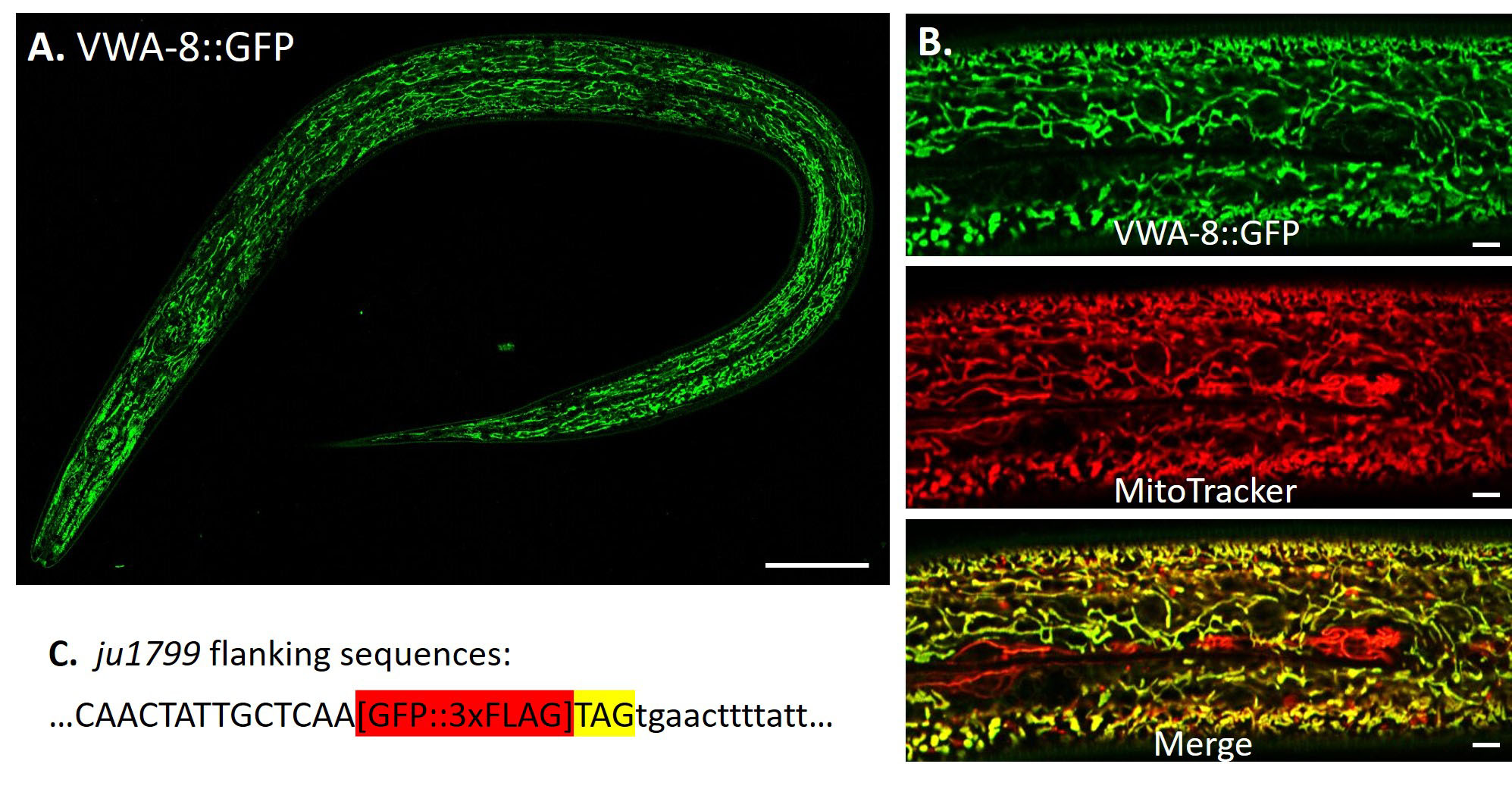
🔋 Muscle Mitochondrial Morphology
- Mitochondria are assessed for:
- Fragmentation vs. elongation
- Signs of stress or preservation
- Relevant because mitochondrial health is central to muscle maintenance
🐛 Locomotive Behavior
- Measures how worms move (e.g. crawling, thrashing)
- Serves as a functional readout of muscle and neuronal health
- Links structure → function
💤 Dauer Formation
- Dauer is a stress-induced, energy-conserving developmental state
- The study asks whether bear serum:
- Promotes or suppresses dauer entry
- This tests whether serum influences systemic metabolic decisions
🥚 Egg Hatching
- Investigates whether exposure to bear serum:
- Alters egg viability
- Affects developmental timing
- Compared explicitly to PBS controls
- Ensures observed effects are not due to general toxicity
🧪 Controls: PBS
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) is used as a baseline control
- Allows clear separation of:
- Nutritional/protein effects
- Specific bioactive serum factors
🧬 Proteomics: Mechanistic Insight
To connect phenotype with mechanism, the study:
- Analyzes proteomic data from Frøbert et al. (2022)
- Compares:
- 🟢 Summer bear blood
- 🔵 Winter bear blood
- Goal:
- Identify seasonally regulated proteins
- Propose plausible molecular explanations for:
- Muscle preservation
- Metabolic suppression
- Stress resistance during hibernation
This step bridges observed worm phenotypes ↔ real bear biology.
🧠 Big Picture Takeaway
This project:
- Tests a cross-species serum-transfer hypothesis
- Uses C. elegans as a minimal, mechanistic discovery platform
- Integrates:
- Physiology 🧍
- Behavior 🐛
- Cell biology 🔬
- Proteomics 🧬
- Aims to uncover systemic, circulating factors that protect muscle during prolonged inactivity
If successful, it provides a foundation for understanding hibernation-inspired muscle preservation—with potential relevance to aging, immobilization, and spaceflight 🚀